 Abengoa
Abengoa
Annual Report 2012
In order to make sure that the company is running smoothly and to secure its long-term future, a precise and rigorous management system, in addition to sound strategic planning, is essential, and should take into account the risks associated with the company’s own activity and foresee the way to mitigate these risks.
Along these lines, Abengoa has its own global risk management system in place. Forming part of the common management systems, the system enables risks to be identified and controlled and is updated periodically so as to create a common management culture, fulfill the objectives set in this regard and have the capability to adapt to mitigate any potential risks that may arise in today’s highly competitive environment.
Implementation of this system requires:
- Risk management throughout all levels of the company, without exception.
- Full integration into strategy and systems for meeting established targets.
- Full support from management in evaluating, monitoring and following the guidelines established with respect to managing threats.
This risk management system is formalized and executed through the following three tools:
- The norms of obligatory compliance (NOC).
- The processes of obligatory compliance (POC).
- The Universal Risk Model (URM).
Compliance is ensured through verifications conducted by the Internal Auditing Department, and through the committee meetings held periodically with the company’s senior management and the chairman’s office.

Quality standards form the basis of these instruments, or common management systems, the aim being to comply with international regulations and standards that include ISO 31000 and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and our systems have been certified by firms of international renown.
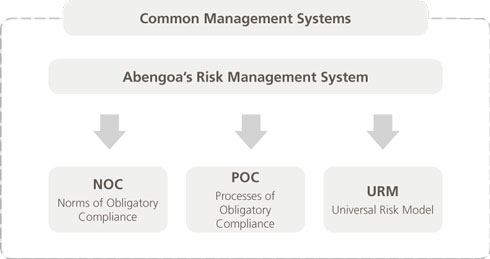
Risk management model

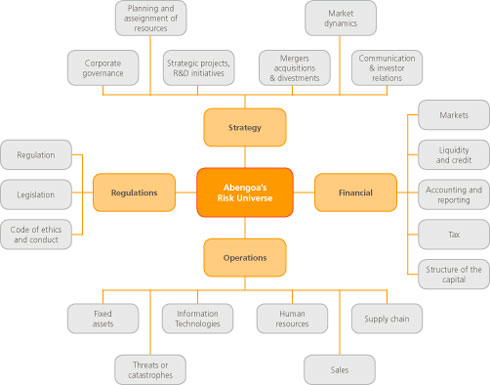
The URM comprises 56 risks belonging to 20 different categories and which are grouped into 4 major areas: finance, strategy, regulations, and operations.
The company reviews the model annually to ensure that the calculations designed for each risk best reflect the company’s reality. This review was conducted in June 2012.
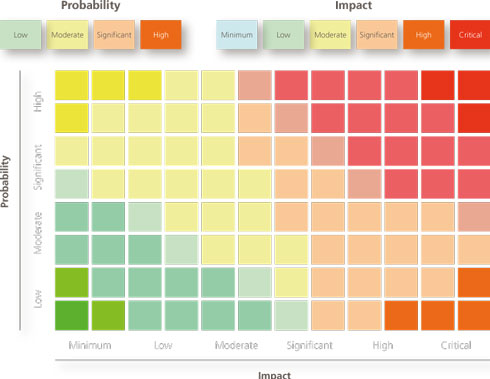
All of the risks included in the URM are evaluated on the basis of two criteria:
- Probability of occurrence: Degree of frequency with which it can be assured that a given cause will bring about an event with a negative impact on Abengoa.
- Impact on the company: Set of potential negative effects on the company’s strategic objectives.
The computer application Archer eGRC, which automates the process of identifying, evaluating, addressing, monitoring and reporting on the risks that make up the company’s URM, was consolidated in 2012 as the chosen instrument for computing and reporting on the risks across company activities and sectors. Work is currently under way to synchronize the application with other corporate tools.
Managing CSR risks at Abengoa facilities
In 2010, Abengoa developed a system to determine, oversee and control potential risks involving CSR and affecting the company’s facilities. In 2011, four pilot projects were implemented at India, Brazil, Huelva and Seville (Spain).
Risk assessment was performed in 2012 for all of the company’s relevant facilities.
The risks defined through the system were selected on the basis of issues of relevance to CSR that are identified in the Strategic Plan and which encompass the following areas:
- Labor practices.
- Occupational health and safety.
- Suppliers.
- Social engagement and local impact.
- Environmental management and climate change.
- Ethics, integrity and compliance.
After examining 52 facilities, the consolidated results found the following risks to exist on a global scale:
- 16 highly material risks that include environmental certifications among suppliers, contractors, collaborating companies and other partners; potential emergency situations or contingency plans drawn up for environmental incidents.
- 104 moderately material risks that include upholding human rights among suppliers, contractors, collaborating companies and other partners; supplier failure to comply with health and safety standards or generation of negative impacts on the communities present in their sphere of influence.
- 173 risks of low materiality related to the environmental impact of Abengoa’s activities; employee training and skills; and environmental management systems.
The results of these periodic risk assessments will enable each Abengoa facility to step up efforts towards mitigating the risks flagged as material in their specific area of activity.
Abengoa's Universal Risk Model arrangement.
Visual representation of risks valiation.
© 2012 Abengoa. All rights reserved
